What is an Endoscope Camera Used For? The Top 15 Applications
How can you inspect small, hidden spaces inside an object without disassembling it? I believe everyone has thought about this question, and the answer to this problem is an endoscope camera.
Endoscope cameras, commonly known as "borescope cameras" or "snake cameras", are multi-functional tools equipped with a miniature camera and light source at the end of a flexible cable. This unique design allows it to carefully detect small, inaccessible places inside an object without disassembling the object.
As a quality control inspector, I have extensive experience in using endoscope cameras for practical operations, so I understand the role of this tool in different inspection fields. For example, the common applications of endoscope cameras that we can access in life are medical diagnosis and automotive inspection.
In this article, we will learn how endoscope cameras are used in different industries and why they are so important in these industries. The following are the top 15 applications of endoscope cameras, and we will learn about them one by one.
Top 15 Endoscope Camera Applications
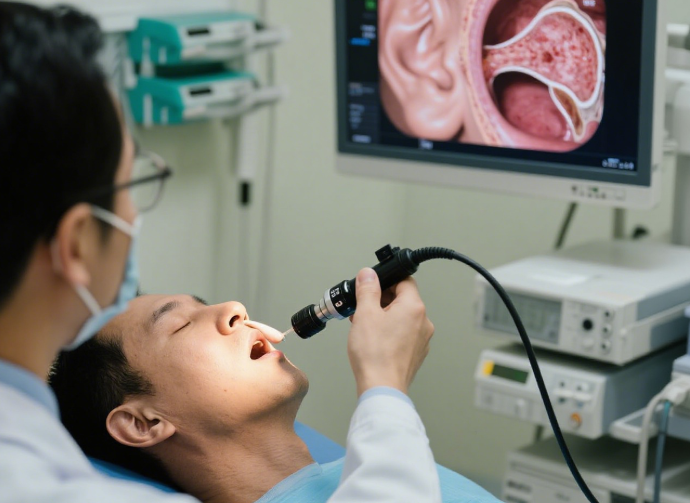
1. Medical Diagnosis and Surgery
This is the original and most critical endoscope camera application. Doctors use specialized endoscopic cameras for procedures to visualize internal organs and tissues without invasive surgery.Sinoseen has an endoscope camera specially designed for gynecological examinations. Those who are interested can take a look.
-
Benefits: Minimally invasive, reduced recovery time, lower risk of infection compared to open surgery.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Gastroscopy & Colonoscopy: Examining the digestive tract to detect ulcers, tumors, or inflammation.
-
Bronchoscopy: Visualizing the airways and lungs to diagnose respiratory conditions.
-
Laparoscopy: Performing abdominal surgery through small incisions.
-
2. Plumbing and Pipe Maintenance
A video drain pipe inspection endoscope is a go-to tool for plumbers. It allows them to quickly locate blockages, leaks, or cracks in pipes without having to tear down walls or dig up yards, saving time and money.
-
Benefits: Non-destructive inspection, cost savings, quick problem identification, prevents unnecessary excavation.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Drain Clog Location: Finding the exact position and nature of a clog (e.g., tree roots, grease buildup).
-
Sewer Line Assessment: Inspecting old or broken sewer lines to determine if they need repair or replacement.
-
3. Automotive Inspection
Mechanics use a borescope camera to inspect the internal components of an engine. This helps diagnose issues like carbon buildup or piston damage without the need for a complete engine teardown.
-
Benefits: Faster diagnostics, saves labor hours, avoids costly engine disassembly.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Engine Cylinder Inspection: Checking cylinder walls and piston crowns for wear or damage.
-
Valve & Spark Plug Inspection: Looking for deposits or signs of failure around valves and spark plugs.
-
Transmission Inspection: Viewing internal gearbox components without disassembly.
-
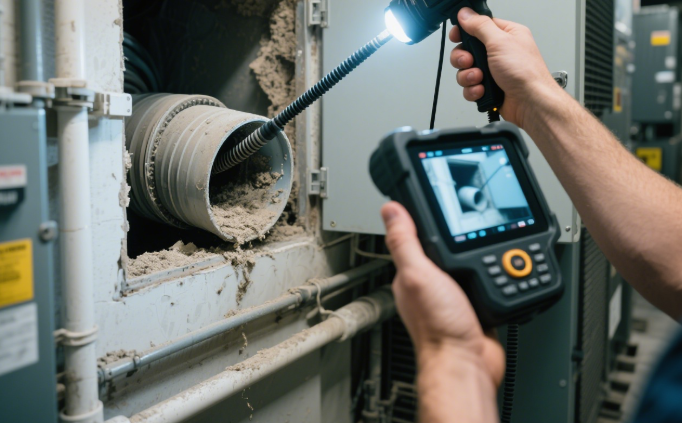
4. HVAC System Inspection
HVAC technicians use these cameras to inspect ducts, vents, and internal components of heating and cooling systems.
-
Benefits: Improves indoor air quality, increases system efficiency, allows for targeted repairs.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Duct Cleaning: Identifying areas with mold, dust, or debris buildup that need to be cleaned.
-
Leak Detection: Finding leaks in evaporator coils or refrigerant lines.
-

5. Home Inspection and Maintenance
Home inspectors and contractors rely on snake cams to look inside wall cavities, under floors, and into attics to check for pests, electrical wiring issues, mold, or structural damage.
-
Benefits: Non-intrusive, provides clear visual evidence of issues, helps prevent minor problems from escalating.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Pest Control: Locating rodent nests or insect infestations inside walls.
-
Mold Detection: Checking for signs of mold growth in hard-to-reach, damp areas.
-
Insulation Integrity: Assessing the condition of insulation in wall cavities.
-
6. Electronics and Electrical Wiring
Electricians use a miniature endoscope camera to snake through electrical conduits and behind walls to trace wiring, identify breaks, or check for potential fire hazards.
-
Benefits: Increased safety, faster troubleshooting, avoids damaging walls or ceilings.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Wire Tracing: Following the path of a wire through a crowded conduit or ceiling void.
-
Junction Box Inspection: Checking connections and looking for signs of overheating or loose wires.
-
7. Search and Rescue Operations
First responders use rugged borescope cameras to search for survivors in rubble after natural disasters or building collapses.
-
Benefits: Enhanced safety for rescuers, locates victims quickly, allows for communication with trapped individuals.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Structural Collapse: Pushing the camera into small voids to check for signs of life.
-
Cave Exploration: Viewing inaccessible cave sections to assess stability.
-
8. Aerospace and Aviation Maintenance
Aviation technicians use high-precision borescope cameras to inspect turbine blades, engine parts, and fuselage structures for cracks or wear without disassembling the aircraft.
-
Benefits: Ensures flight safety, reduces maintenance downtime, saves on costly disassembly and reassembly.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Engine & Turbine Inspection: Checking for cracks, corrosion, or foreign object damage (FOD) on jet engine components.
-
Fuselage Inspection: Examining hidden structural areas for fatigue.
-

9. Manufacturing Quality Control
In manufacturing, these cameras are used to inspect the inside of pipes, castings, welds, and complex components for defects during the quality control process.
-
Benefits: Ensures product integrity, identifies flaws before assembly, reduces waste and recalls.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Weld Inspection: Checking the quality of internal welds in pipes or tanks.
-
Component Inspection: Looking for burrs, cracks, or blockages in small machined parts.
-
10. Animal Health Care and Veterinary Use
Veterinarians use endoscopic cameras for non-invasive examinations of animal airways, digestive tracts, and other internal areas.
-
Benefits: Less stress on the animal, accurate diagnosis without surgery, quicker recovery.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Foreign Body Retrieval: Removing swallowed objects from a pet's throat or stomach.
-
Internal Organ Diagnosis: Examining organs like the esophagus, stomach, or bladder for disease.
-
11. Archaeology and Research
Archaeologists use them to look inside small fissures, rock formations, or delicate artifacts to explore or document findings without disturbing the site.
-
Benefits: Non-destructive exploration, preserves historical sites and artifacts, provides new visual data.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Tomb Exploration: Peering into sealed chambers or burial sites.
-
Fossil Inspection: Examining the internal structure of fossils or rock samples.
-
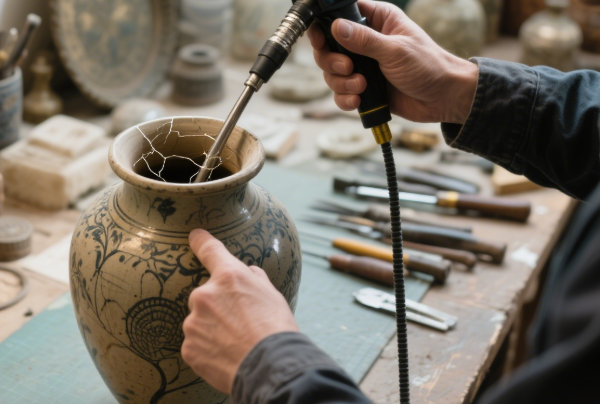
12. Art and Antique Restoration
Conservators and restorers use these cameras to examine the internal structure of valuable antiques, sculptures, or musical instruments without causing damage.
-
Benefits: Protects fragile objects, informs restoration strategies, verifies authenticity.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Violin Repair: Viewing the internal bracing and glue joints of a violin.
-
Furniture Assessment: Checking for internal wood rot or insect damage in antique furniture.
-

13. Chimney and Flue Inspection
Chimney sweeps use these cameras to inspect the inside of chimneys for creosote buildup, blockages, or cracks that could pose a fire risk.
-
Benefits: Prevents chimney fires, ensures safe operation, provides visual proof for cleaning recommendations.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Creosote Level Check: Assessing the thickness of flammable buildup.
-
Crack Detection: Finding dangerous cracks in the flue liner.
-
14. Law Enforcement and Security
Police and bomb squads use endoscopic cameras to peer into suspicious packages, behind doors, or into confined spaces for surveillance or to assess threats from a safe distance.
-
Benefits: Enhanced safety for personnel, provides intelligence before entry, minimizes risk.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Hostage Situations: Viewing a room from under a door.
-
Bomb Disposal: Inspecting suspicious items without direct contact.
-
15. Research and Education
In labs and classrooms, a miniature endoscope camera can be connected to a computer to project a live view of chemical reactions in closed containers or to demonstrate biological processes in real-time.
-
Benefits: Interactive learning, safe observation of hazardous processes, easy data collection for analysis.
-
Specific Applications:
-
Fluid Dynamics: Observing fluid flow in complex, sealed tubing.
-
Biology Labs: Showing students the internal structures of plants or small organisms.
-

Conclusion
From medical diagnosis to daily home maintenance, endoscopic cameras have proven their versatility. Their ability to provide visual observation of tight spaces makes them an indispensable tool for diagnosis, inspection, and repair in a wide range of fields. The continued miniaturization of endoscopic cameras and advances in technology will only further expand their potential applications in the future.
you can view our Endoscope camera module list to learn more info.
Endoscopic cameras from Sinoseen
If you have a demand for endoscopic cameras now, but are worried about the quality difference between samples and bulk orders on the market, then you can seek help from Sinoseen. At Sinoseen, we always take quality as our first production goal. With more than ten years of manufacturing experience, we have been implementing international ISO standards to allow customers to get products with 100% the same quality as the samples. If you are looking for a reliable camera module manufacturer and have strict quality requirements, please contact us now!

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 SR
SR
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 IS
IS
 AZ
AZ
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 HA
HA
 LO
LO
 MR
MR
 MN
MN
 PA
PA
 MY
MY
 SD
SD















