Understanding the Difference Between Parallel Interface and Serial Interface
I. Introduction
A. Basic Concepts of Serial and Parallel Interfaces
In the realm of digital communication, serial and parallel interfaces represent two fundamental methods for transmitting data between devices.
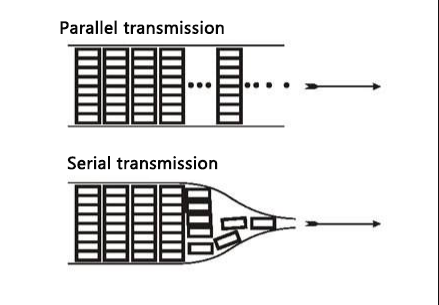
A serial interface operates by sending data one bit at a time over a single channel, sequentially. Conversely, a parallel interface transmits multiple bits simultaneously over multiple channels.
B. The Importance of Understanding the Difference Between Serial and Parallel Interfaces
Understanding the disparities between serial and parallel interfaces is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it enables informed decision-making when selecting the appropriate interface for specific applications. Secondly, it aids in optimizing data transmission efficiency and reliability by matching the interface with the requirements of the task at hand. Lastly, as technology evolves, knowing the nuances between these interfaces can guide advancements in communication protocols and hardware design.
In summary, discerning the variances between serial and parallel interfaces empowers engineers, developers, and technology enthusiasts to leverage the most suitable interface for achieving optimal performance in diverse digital communication scenarios.
After understanding these basics, do you have a clear understanding of whether to choose a serial interface camera or a parallel interface camera module?If you are still in doubt, read on.
II. Characteristics of Parallel Interface
A. Working Principle of Parallel Transmission
In parallel transmission, data is transferred simultaneously across multiple channels, with each channel dedicated to a specific bit of the data. This allows for higher data transfer rates compared to serial transmission.
B. Advantages and Disadvantages of Parallel Interface
Advantages:
- High data transfer rates, especially for short distances.
- Suitable for applications requiring simultaneous transmission of multiple data bits.
- Generally simpler protocol compared to serial interfaces.
Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to signal interference and crosstalk due to the proximity of multiple channels.
- Higher cost and complexity associated with multiple data lines and synchronization requirements.
- Limited scalability for longer distances due to signal degradation.
C. Wide Applications of Parallel Interface
Parallel interfaces find extensive use in scenarios where high-speed data transfer over short distances is critical. Common applications include:
- Internal computer communication (e.g., between CPU and memory).
- High-performance computing systems.
- Graphics processing units (GPUs).
- Interfacing with high-speed peripherals like printers and scanners.
III. Characteristics of Serial Interface
A. Working Principle of Serial Transmission
In serial transmission, data is sent sequentially over a single channel, bit by bit. Each bit is encoded with start and stop bits to facilitate synchronization between the transmitter and receiver.
B. Advantages and Disadvantages of Serial Interface
Advantages:
- Longer transmission distances with minimal signal degradation.
- Lower cost and simpler wiring compared to parallel interfaces.
- Greater scalability for long-distance communication.
- Reduced susceptibility to signal interference due to single-channel transmission.
Disadvantages:
- Slower data transfer rates compared to parallel interfaces.
- Increased complexity in protocol implementation for synchronization and error detection.
- Less efficient for applications requiring simultaneous transmission of multiple data streams.
C. Wide Applications of Serial Interface
Serial interfaces are ubiquitous in various industries and applications due to their versatility and reliability. Common applications include:
- External device connectivity (e.g., USB, Ethernet, HDMI).
- Networking equipment (e.g., routers, switches).
- Long-distance communication (e.g., telecommunications, satellite communication).
- Data storage interfaces (e.g., SATA, PCIe).
IV. Comparison Between Parallel and Serial Interfaces
A. Comparison of Data Transfer Speed
Parallel Interface:
- Offers higher data transfer rates due to simultaneous transmission of multiple bits.
Serial Interface:
- Typically slower data transfer rates compared to parallel interfaces due to sequential bit-by-bit transmission.
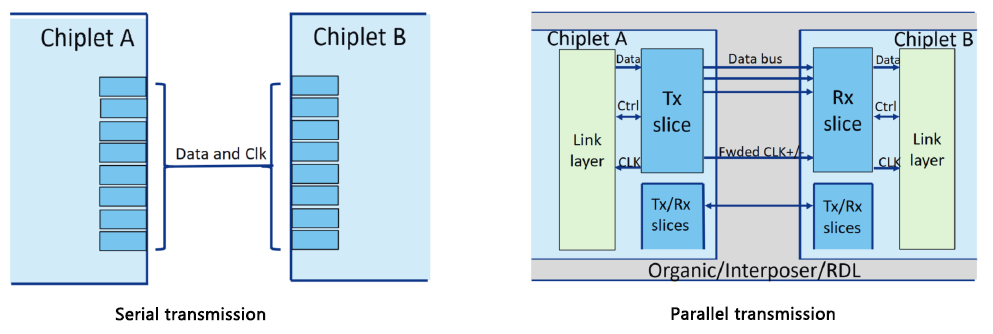
B. Comparison of Data Transfer Distance
Parallel Interface:
- Limited by signal degradation over longer distances.
Serial Interface:
- Can achieve longer transmission distances with minimal signal degradation.
C. Comparison of Application Domains
Parallel Interface:
- Commonly used in applications requiring high-speed data transfer over short distances, such as internal computer communication and high-performance computing.
Serial Interface:
- Widely applied in scenarios necessitating long-distance communication, external device connectivity, and data storage interfaces.
D. Cost Comparison
Parallel Interface:
- Generally entails higher costs due to the complexity of wiring and synchronization requirements.
Serial Interface:
- Tends to be more cost-effective with simpler wiring and lower hardware complexity.
V. Future Development Trends of Parallel and Serial Interfaces
A. Technological Development Trends
Parallel Interface:
- Continual efforts to improve data transfer rates and reduce signal interference.
Serial Interface:
- Advancements focused on enhancing transmission efficiency and addressing evolving communication standards.
B. Changes in Application Domains
Parallel Interface:
- Shift towards specialized applications requiring high-speed parallel communication, such as graphics processing and high-performance computing.
Serial Interface:
- Increasing adoption in emerging technologies like IoT and telecommunications for long-distance data transmission.
C. Potential Technological Trends
Parallel Interface:
- Exploration of hybrid parallel-serial interface solutions to balance speed and distance requirements.
Serial Interface:
- Integration of advanced error correction and data compression techniques to enhance transmission efficiency.
VI. Conclusion
A. Summarizing the Differences and Application Scenarios of Parallel and Serial Interfaces
Understanding the differences between parallel and serial interfaces is crucial for selecting the most suitable interface for specific application requirements. While parallel interfaces offer high-speed data transfer over short distances, serial interfaces excel in long-distance communication with cost-effective and scalable solutions.
B. Future Development Outlook
As technology continues to evolve, both parallel and serial interfaces will undergo further advancements to meet the growing demands of modern communication systems. By staying abreast of emerging trends and technological innovations, stakeholders can leverage the strengths of parallel and serial interfaces to drive innovation and efficiency in diverse application domains.
If you are looking for a cost-effective camera module solution, feel free to contact us.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 SR
SR
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 IS
IS
 AZ
AZ
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 HA
HA
 LO
LO
 MR
MR
 MN
MN
 PA
PA
 MY
MY
 SD
SD















