The difference between PDAF Camera vs. OIS Camera:A begin`s guide
For embedded vision, achieving clear, stable image quality is key. Two vital technologies, PDAF camera (Phase Detection Autofocus) and OIS camera (Optical Image Stabilization), address distinct challenges: focusing speed and image blur. Engineers designing camera modules must grasp PDAF camera vs OIS camera nuances. This article clarifies PDAF camera meaning, explains OIS camera meaning, and helps decide which is better OIS or PDAF for your application.
What is a PDAF Camera?
So, what is a PDAF camera? A PDAF camera uses Phase Detection Autofocus for fast, accurate focusing. Unlike older systems, PDAF measures phase differences in light rays entering the lens. This helps the camera module instantly calculate needed focus adjustments, reducing "focus hunting."
This technology integrates specialized pixels, or pixel pairs, directly onto the image sensor. These photodiodes detect light from opposite sides of the lens, acting as tiny rangefinders. This phase difference enables near-instant autofocus for the camera module.
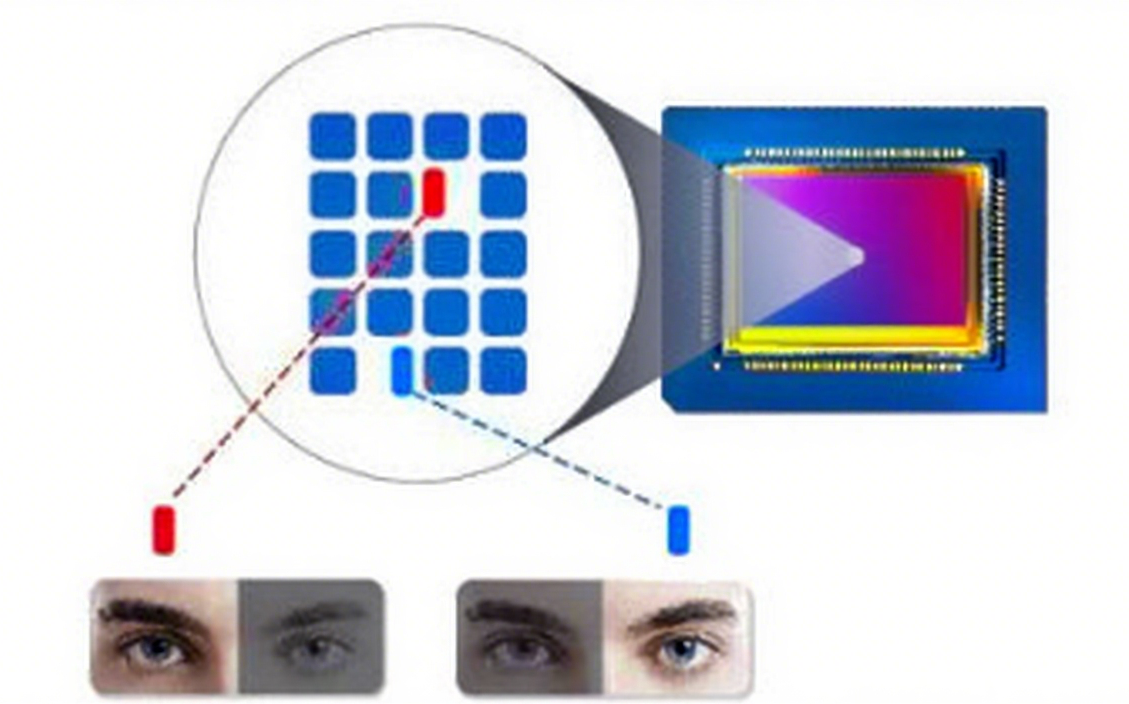
PDAF Camera Meaning: Accelerating Autofocus Performance
The core PDAF camera meaning centers on speed and precision. By directly measuring subject distance, PDAF moves lens elements quickly to the correct position. This makes it ideal for fast-moving subjects or applications needing immediate focus lock.
For embedded vision systems—like robotics or automotive cameras—fast, reliable autofocus is a common issue. A PDAF camera ensures sharp focus even in dynamic settings. This boosts accuracy for image processing, such as object recognition. The market for advanced autofocus, including PDAF, continues robust growth, driven by demand for better imaging in smart devices and industrial automation.
What is the Meaning of OIS? Combating Blur from Motion
Now, what is the meaning of OIS? OIS stands for Optical Image Stabilization. This technology physically shifts lens elements or the image sensor to counteract camera movement. When the camera module detects subtle shakes via built-in gyroscopes, the OIS system moves optical components in real-time. This keeps the projected image steady on the sensor.
This mechanical compensation greatly reduces blur, crucial in low-light or during video recording. Without OIS, minor hand tremors or vibrations degrade image quality and data utility.
OIS Camera Meaning: Ensuring Image Stability
The OIS camera meaning emphasizes stability and blur reduction. By actively compensating for motion, an OIS camera captures sharper images and smoother video. This benefits scenarios needing longer exposures or when the camera module is on an unstable platform.
For embedded vision, OIS is vital in handheld tools, vibration-prone security cameras, or camera modules in drones and autonomous vehicles. It ensures clear data acquisition despite instability. This enhances reliability for surveillance, robotic navigation, and visual inspection. The global optical image stabilization market projects substantial growth, with a CAGR around 10% by 2029 (Source: MarketsandMarkets, "Optical Image Stabilization Market - Global Forecast to 2029", published April 2024).
Which is Better OIS or PDAF? Two Different Purposes
When asking "Which is better OIS or PDAF?" it's not about superiority, but synergy. They serve fundamentally distinct yet complementary purposes. PDAF ensures subject sharpness, while OIS maintains overall image stability from camera movement.
-
PDAF excels at: Quick, precise focus on subjects, especially moving ones. It fixes blurry subjects from slow focus.
-
OIS excels at: Reducing motion blur from camera shake, particularly in low light or video. It fixes blurry images from an unsteady camera.
Many high-performance camera modules integrate both. PDAF provides sharp focus, and OIS ensures stability, offering a comprehensive solution for challenging visual environments.
Technical Implementations and Considerations
Understanding the mechanics of both PDAF camera and OIS camera systems is vital for engineers.
PDAF Implementation
PDAF uses dedicated photodiodes or pixel pairs on the image sensor. These autofocus pixels capture light from different lens pupil sides. Comparing their phase shift, the system determines focus error and lens movement direction. This commands an actuator, often a Voice Coil Motor (VCM), to rapidly adjust lens position. This fixes slow, "hunting" autofocus, which causes missed shots or inaccurate data. Its key benefit is near-instant focus lock.
OIS Implementation
OIS typically employs tiny gyroscopes within the camera module to detect angular movements. Upon detection, an actuator, frequently a voice coil motor (VCM), precisely shifts optical elements—either a lens group or the image sensor—in real-time. This optical shift compensates for motion, keeping light rays stable on the sensor. OIS mitigates blur from handshake or minor vibrations, a common problem for handheld or vehicle-mounted camera modules. Its strong selling point is improved low-light performance and superior video stability without faster shutter speeds or higher ISO.
PDAF Camera vs OIS Camera: A Direct Comparison
For engineers needing a swift overview, here’s a direct comparison of PDAF camera and OIS camera technologies:
Tips for Choosing Between PDAF or OIS
Selecting between, or combining, a PDAF camera and an OIS camera critically depends on your embedded vision application's core needs. Consider these expert tips:
-
Prioritize Autofocus Speed? Choose PDAF. If your camera module must quickly lock onto and track dynamic objects (e.g., automated inspection, robotics), PDAF camera technology is essential. It minimizes "hunting" for focus, ensuring critical data capture.
-
Struggling with Motion Blur? Opt for OIS. When your camera module operates in unstable environments (e.g., vehicle-mounted cameras, handheld devices) or in low light, OIS camera technology becomes invaluable. It stabilizes the image, preserving image quality despite movement.
-
Need Both? Integrate Them! For comprehensive performance in dynamic and challenging settings, a camera module with both PDAF and OIS offers the most robust solution. This combines sharp, fast focus with stable, blur-free images, addressing multiple pain points for superior data acquisition.
-
Consider Cost and Complexity: While ideal, integrating both technologies adds to the camera module's cost and complexity. Evaluate your project budget and system constraints. Sometimes, optimizing lighting or mechanical stability might be a more cost-effective alternative.
-
Test in Real-World Conditions: Always prototype and rigorously test your chosen camera module in its actual operating environment. Real-world conditions often reveal unexpected challenges, providing invaluable guidance for your final decision between PDAF camera or OIS camera solutions. This ensures optimal system performance.
Conclusion: Tailoring Technologies to Your Camera Module Needs
The debate of PDAF camera vs OIS camera isn't about superiority, but synergy. Both are indispensable for optimal image quality in modern embedded vision applications. Understanding PDAF camera meaning reveals its power in rapid focusing, while OIS camera meaning highlights its crucial role in image stabilization. For engineers, deciding which is better OIS or PDAF boils down to assessing your system's primary challenge: fast-moving subjects, unstable platforms, or both?
Often, the best camera module strategically incorporates both PDAF and OIS, providing a comprehensive solution for autofocus speed and image stability. Therefore, carefully consider your application's specific demands—its environment, subject motion, and typical lighting—to select the ideal combination of these powerful optical technologies.
Ready to enhance your embedded vision project with superior autofocus and image stabilization? Contact our experts today for tailored guidance on integrating the right PDAF camera and OIS camera solutions to elevate your camera module's performance to the next level.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 SR
SR
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 IS
IS
 AZ
AZ
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 HA
HA
 LO
LO
 MR
MR
 MN
MN
 PA
PA
 MY
MY
 SD
SD















